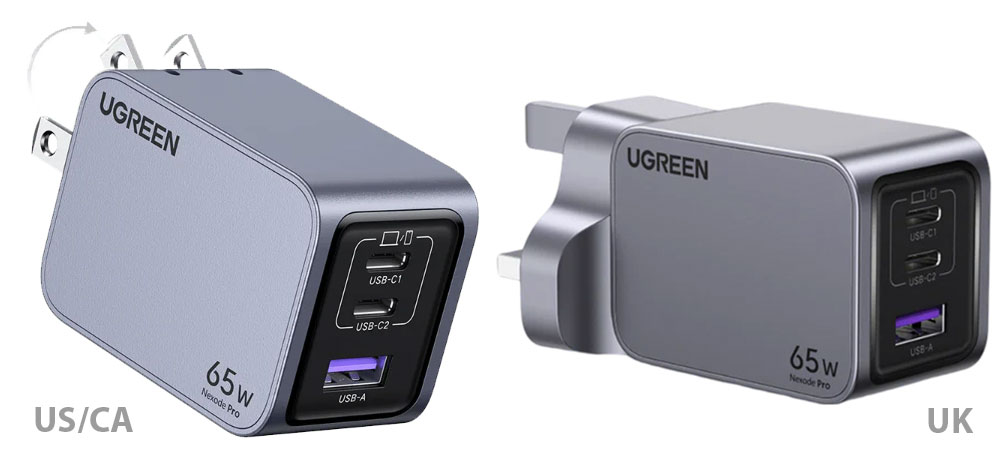
USB Type-C is the most flexible connection for notebooks and smartphones. The most important of its many capabilities is as a charging socket for battery-powered devices. USB-C should finally make everything simple: One socket, one cable, one power supply for all devices – from computers to smartphones and tablets to headphones and other peripherals.
So much for the theory, which always sounds simple with USB. The reality is more confusing.
Not every USB-C power supply is suitable for every device. Not all Type-C ports can be used to charge devices quickly or at all. And not every Type-C cable ensures reliable power transmission.
This guide will give you an overview of the technical possibilities of Type-C charging and recommends suitable power supply units for all devices. If you’d like to avoid all the background and simply know which cords as worth your hard-earned money, be sure to check out our roundup of the best USB-C cables. We perform hands-on tests that go far deeper than most other sources on the web.
Further reading: Buying a USB-C cable? Look out for these 6 gotchas!
USB Type-C: The standard connection for charging
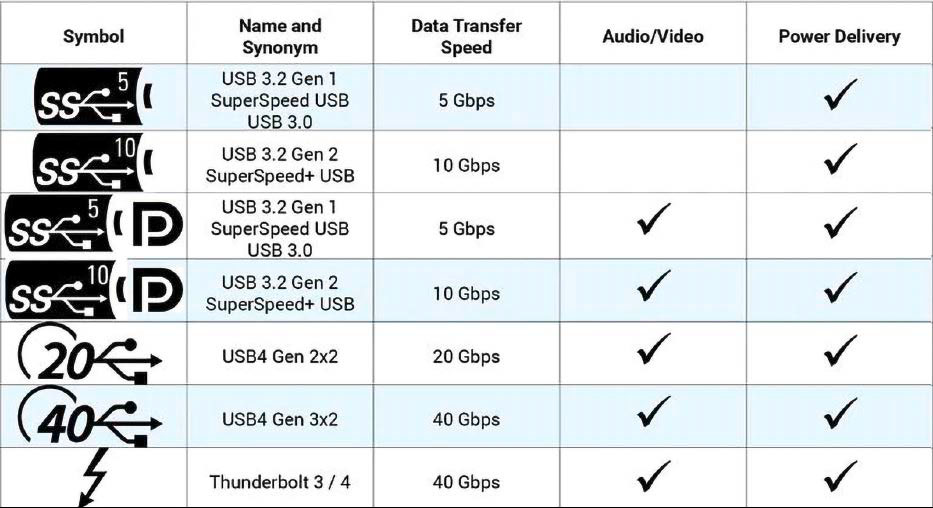
There are many symbols that identify a USB-C port on a laptop as a charging port. In practice, however, you will usually only find the Thunderbolt lightning bolt (at the bottom) on the housing.
IDG
Almost all mobile devices can now be charged via USB Type-C: For smartphones, Apple was the last major manufacturer to switch from the proprietary Lightning connector to USB-C last year with the iPhone 15.
Apart from that, there are only very cheap bargain smartphones that still rely on micro USB as a charging port. The situation is similar for tablets, where market leader Apple already favored USB-C over Lightning three years ago with the iPad 9. You will also hardly find any devices without USB-C for headphones, ebook, readers, and mobile speakers.
Only laptops still have numerous models that do not use Type-C to charge the battery: These are often older model series from the entry-level range. More frequently, however, USB-C is not the main connection for charging.
Although powerful gaming and multimedia laptops have USB-C, they also have a dedicated power connection with a higher charging capacity that fits the power supply unit supplied. Business laptops with a USB-C port and power supply unit often still have the hollow plug connection so that companies can continue to use power supply units from decommissioned models.
A Type-C connection on a laptop also does not always handle power delivery. The only way to find out whether a Type C socket is capable of power delivery is to look at the technical data. A Type-C port with Thunderbolt supports charging in any case.
Further reading: We tested 43 old USB-C to USB-A cables. 1 was great. 10 were dangerous
Advantages of power delivery via USB-C
The triumph of Type-C is easy to explain, as the connection offers numerous advantages for users and manufacturers:
- Cables can be connected quickly and easily because the symmetrical plug is twist-proof.
- The socket takes up little space so that devices can be made lighter and flatter.
- And as Type-C can handle data and video transmission as well as charging, ideally a single cable is all that is needed between the computer and peripherals, which keeps the desk tidy.
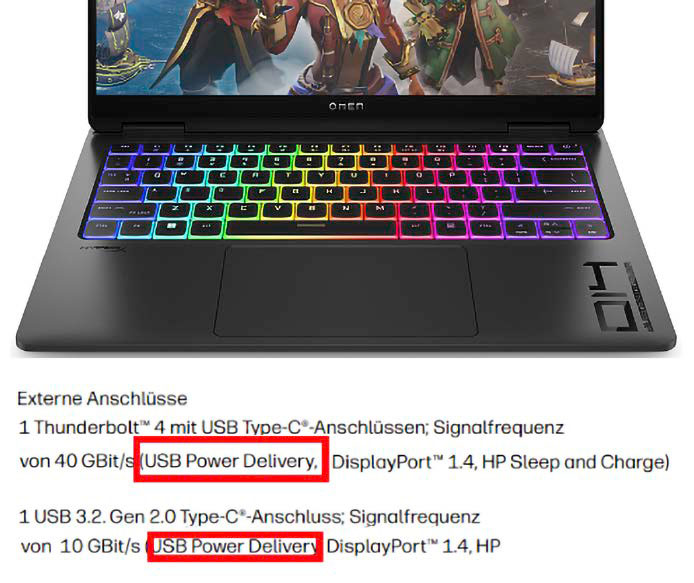
Whether a mobile device supports USB-C Power Delivery is usually stated in the technical data for the connections. If so, you can use a suitable power adapter for charging.
IDG
Devices can also be charged faster with USB-C: Power supply units for micro USB only deliver up to 10 watts, while chargers with a Type A connection usually deliver 15 to 18 watts. Type-C, on the other hand, supports the improved USB Power Delivery (PD) transmission protocol, which usually allows charging capacities of up to 100 watts and even up to 240 watts in the current version.
our favorite Usb-c Charging cable
Belkin BoostCharge 240-watt charging cable

However, this does not apply to all Type-C connections, devices, and cables: Although everything fits together mechanically, not every combination has to provide the optimum charging power — for example, because different levels of the Power Delivery standard are supported or devices and power supply units do not implement the standard correctly.
USB-C and Power Delivery: How the charging technology works
The technical basis for charging via USB-C is the USB Power Delivery (USB PD) standard. It specifies voltage levels of 5 to 48 volts and currents of 3 or 5 amps in so-called “power profiles” or “power rules.” Depending on the power supply unit, power cable, and device, charging capacities of between 10 and 240 watts are possible.
A typical smartphone power supply unit with 30 watts, for example, offers power profiles for a charging capacity of 15, 27, and 30 watts, while a laptop power supply unit also offers power profiles for 45, 60, 65, or 100 watts.
Before transmission begins, the power supply unit (source) and consumer (sink) agree on the required voltage and current: The power supply unit first checks the cable to see whether it can transmit up to 3 or 5 amps and provides a basic voltage of 5 volts.
It then tells the consumer what other voltages it can supply. The consumer answers which one it needs so that both can agree on a suitable power profile.
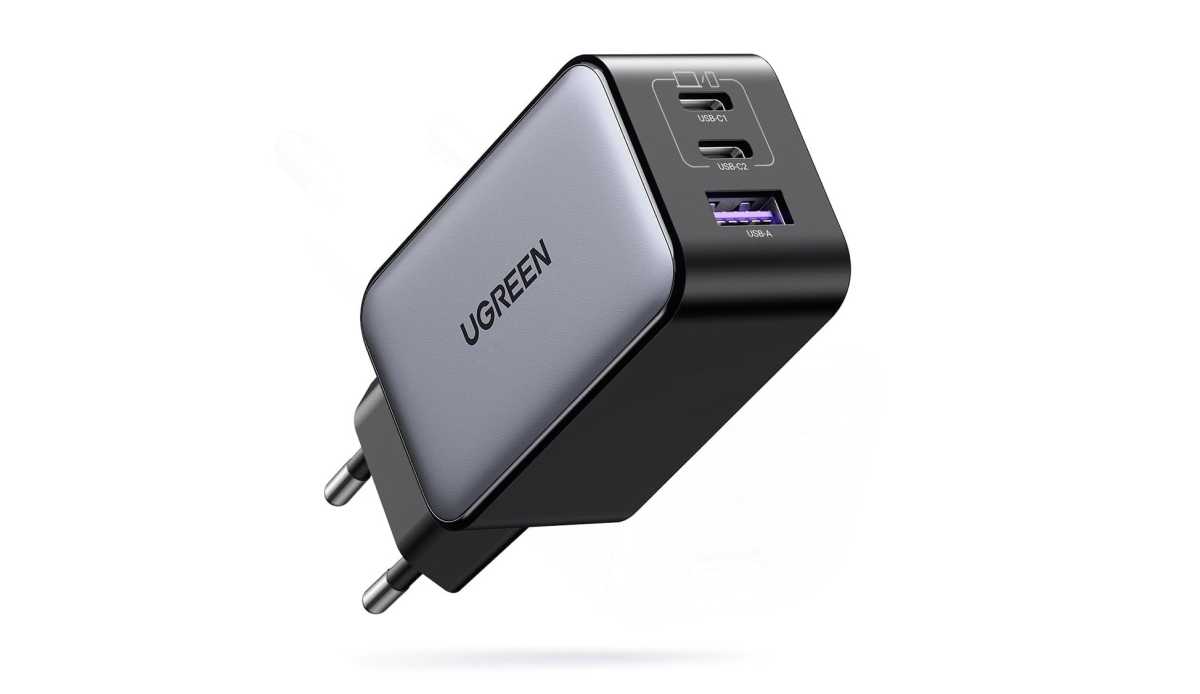

Some multiple power supply units, such as this one from Ugreen, use the semiconductor material gallium nitride (GaN): this allows them to be built very compactly despite their high charging power.
Ugreen
Ideally, any USB-C power supply will charge the device with a Type-C charging socket with optimum performance and as quickly as possible. Even if the power supply does not completely fulfil the requirements of the device, it should provide a minimum charging power, even if the charging process then takes longer.
Conversely, it does not speed up the charging process to use a power supply unit that offers a higher output than the device requires because the consumer cannot call it up.
Since version 3 of USB PD, the power supply unit and consumer can adjust the voltage and current more dynamically. To do this, both must support the optional standard extension PPS (Programmable Power Supply Protocol).
Login to add comment
Other posts in this group

What was Microsoft’s best Windows operating system of all time?

Microsoft has arguably done more to shape the evolution of the PC tha

“The coolest code I’ve ever written.” With these words, Bill Gates in

Updated on April 3, 2025: The new version of Microso

Artificial intelligence has basically taken over and replace traditio

With the warmer months coming up, I’m looking forward to spending mor

